 December 17, 2024
December 17, 2024
In industrial settings, maintaining clean air is essential to ensure safety, product quality, and compliance with regulations. One of the most effective tools for achieving this is the HEPA filter. But what exactly is a HEPA filter, and why is it so important? In this guide, we'll explore the meaning of HEPA, how HEPA filtration works, the different types of HEPA filters, and much more.
A HEPA filter stands for High-Efficiency Particulate Air filter. These filters are specifically designed to remove 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. HEPA filters are widely used in industries where air purity is critical, such as pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace.
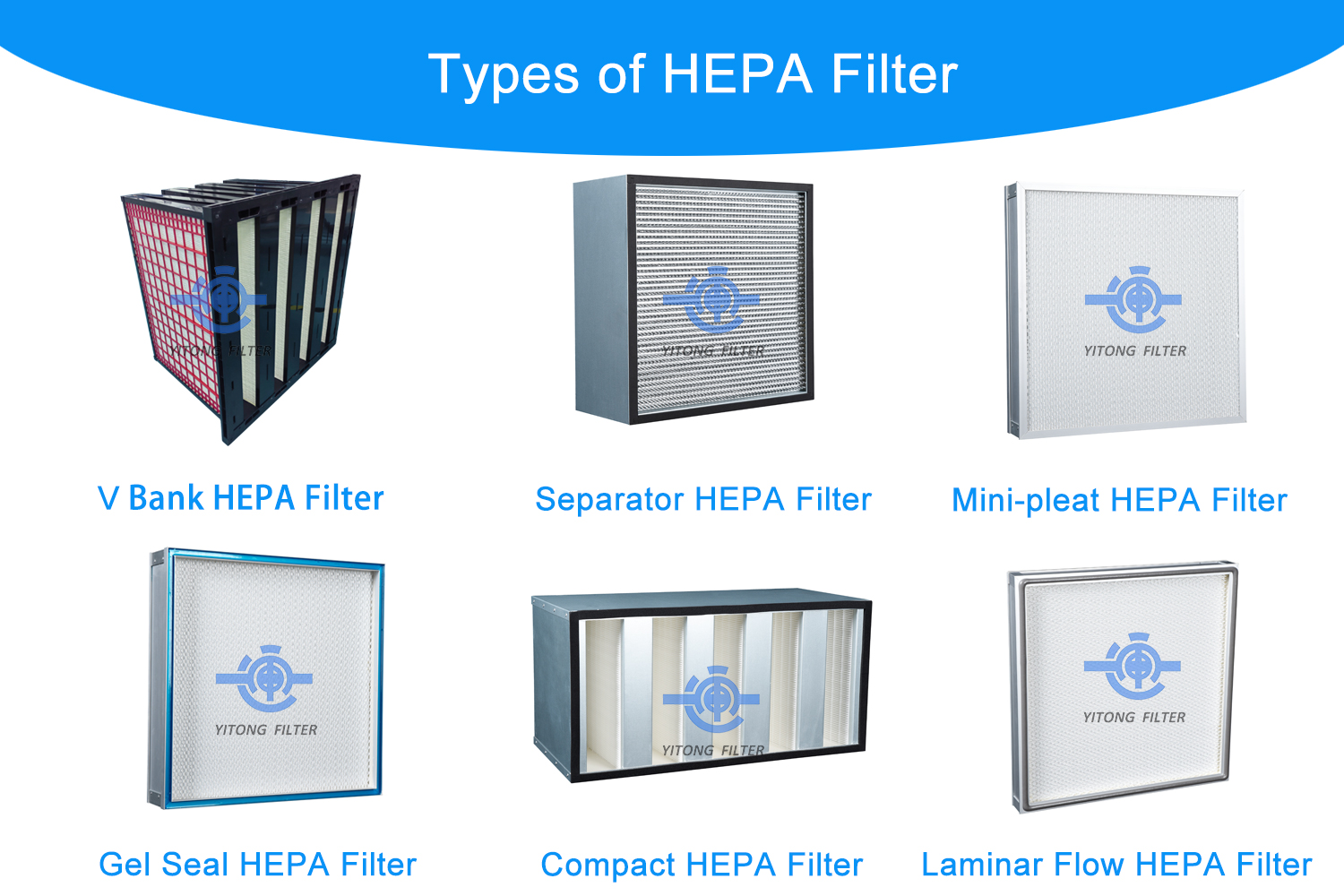
The term HEPA filter refers to an air filter that meets strict standards for particle removal efficiency. HEPA filtration is known for capturing microscopic contaminants like:
- Dust
- Pollen
- Mold spores
- Bacteria
- Viruses
This high level of filtration makes HEPA filters indispensable in environments requiring sterile air.
HEPA filters work by forcing air through a dense mesh of fine fibers. These fibers trap contaminants using three primary mechanisms:
1. Interception: Small particles stick to fibers when they pass close enough.
2. Impaction: Larger particles collide directly with fibers and get trapped.
3. Diffusion: Tiny particles move erratically (Brownian motion) and are captured more easily by the fibers.
This combination allows HEPA air filters to trap particles of various sizes effectively.
HEPA filters are rated based on their ability to capture particles as small as 0.3 microns. To put this in perspective:
- 1 micron = 1/1000th of a millimeter.
- A human hair is about 70 microns thick.
- Bacteria typically range from 0.3 to 5 microns.
The 0.3-micron size is considered the most penetrating particle size (MPPS), meaning it’s the hardest size for a filter to capture. If a HEPA filter can trap 99.97% of these particles, it can effectively capture larger and smaller particles, making it highly efficient.
HEPA filters come in various types, each suited for different applications:
1. True HEPA Filters
These filters meet the standard of capturing 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. They are commonly used in industrial and medical environments.
2. HEPA-like Filters
These do not meet the strict HEPA standard but still provide relatively high filtration efficiency. They are often found in consumer-grade air purifiers.
3. H13 and H14 HEPA Filters
These are classified under the European filtration standards:
- H13 captures 99.95% of particles.
- H14 captures 99.995% of particles.
4. Industrial HEPA Filters
Designed for heavy-duty environments, these filters handle higher airflow volumes and provide robust performance under demanding conditions.
When choosing a HEPA filter, you might encounter terms like HEPA filter and True HEPA filter. Here’s the difference:
- True HEPA Filter: Certified to capture 99.97% of particles at 0.3 microns.
- HEPA Filter: A general term that may or may not meet the strict True HEPA standards.
- True HEPA: Guaranteed performance with certifications.
- Regular HEPA: Might offer good filtration but lacks certification.
For industrial applications, always opt for True HEPA filters to ensure maximum air purity.
HEPA Filtration Systems in Industrial Settings
A HEPA filtration system integrates HEPA filters into an industrial setup to purify air in:
- Cleanrooms
- Hospitals
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Electronics Production
These systems ensure that air contaminants do not compromise the environment or products.
HEPA Ventilation Systems
In industries, HEPA ventilation systems circulate clean, filtered air to maintain air quality standards. This is crucial in areas where dust, chemicals, or biological contaminants are present.
What is a HEPA Filter Mainly Used For?
HEPA filters are used in various industries to ensure air purity and safety:
1. Healthcare: To prevent the spread of infections in hospitals.
2. Pharmaceuticals: To maintain sterile conditions during drug manufacturing.
3. Electronics: To avoid contamination of sensitive components.
4. Food Processing: To ensure hygiene and product quality.
5. Aerospace: To maintain clean air in aircraft cabins.
HEPA filters come in different sizes to fit various applications. Common industrial HEPA filter sizes include:
- 24 x 24 inches
- 12 x 24 inches
- Custom sizes for specific systems
Choosing the right size ensures optimal airflow and filtration efficiency.

HEPA Standards
To be classified as a HEPA filter, the filter must meet specific standards:
- U.S. DOE Standard: 99.97% efficiency at 0.3 microns.
- European EN 1822 Standard: H13 and H14 classifications for industrial use.
- ISO Standards: For international applications.
HEPA-Certified Filters
Always look for filters that meet official HEPA standards to ensure you are getting a product that delivers on its promises.
To maintain efficiency, HEPA filters need regular maintenance:
- Replacement: Depending on usage, replace filters every 6-12 months.
- Inspection: Regularly check for damage or clogging.
- Cleaning: Industrial HEPA filters are often non-washable; replace rather than clean them.
Industrial HEPA filters play a crucial role in maintaining clean air in critical environments. From understanding HEPA filter meaning to knowing the differences between True HEPA filters and regular HEPA filters, this guide covers everything you need for making informed decisions.
By choosing the right HEPA filtration system and maintaining it properly, you can ensure a safer, cleaner workplace and meet industry standards with confidence.
 Aug. 07, 2023
Primary Efficiency Air Filter G4
Aug. 07, 2023
Primary Efficiency Air Filter G4
 Jan. 03, 2025
Semiconductor Fabrication Cleanroom Filters: Ensuring Purity in High-Tech Manufacturing
Jan. 03, 2025
Semiconductor Fabrication Cleanroom Filters: Ensuring Purity in High-Tech Manufacturing
 Sep. 19, 2024
The Importance of HEPA Filters in Hospitals
Sep. 19, 2024
The Importance of HEPA Filters in Hospitals

