 October 30, 2024
October 30, 2024
In a world where indoor air quality (IAQ) is crucial for health and productivity, pocket filters have become essential components of HVAC systems. These high-efficiency filters are widely used in commercial, industrial, and residential environments to ensure clean, breathable air. Pocket filters, also known as bag filters, not only enhance air quality but also contribute to energy savings and airflow optimization.
This blog dives deep into pocket filters, covering their design, key benefits, ISO 16890 standards, maintenance practices, and best use cases to help you choose the right filter for your needs.
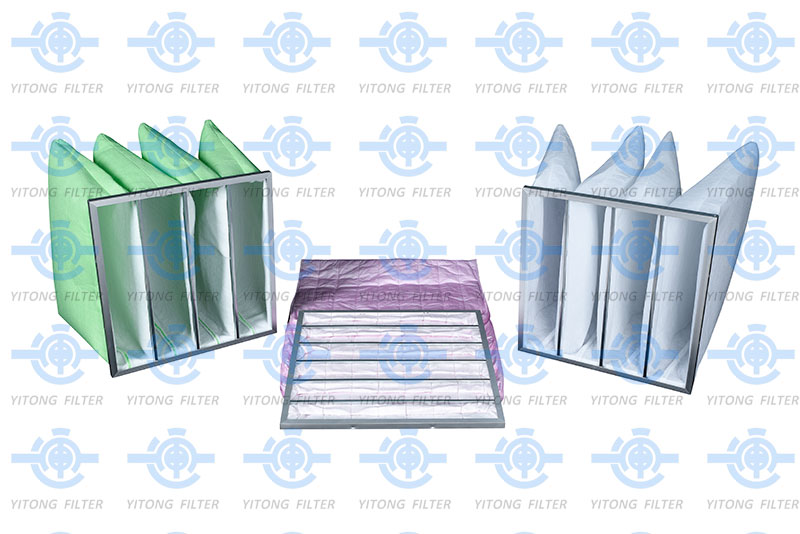
Pocket filters are multi-pocket air filters designed to capture and retain fine particles such as dust, pollen, and even bacteria. They are used in air handling units (AHUs), industrial HVAC systems, and cleanroom environments to maintain high IAQ.
These filters consist of several pleated filter bags (or pockets) that provide an extended surface area, improving dust-holding capacity and lowering airflow resistance. V-bank pocket filters are another variant that uses a V-shaped arrangement to maximize filtration while maintaining a compact size.
Filter Media: Typically made from synthetic fibers or glass fibers.
Pockets/Bags: Multiple layers or pockets allow greater dust accumulation.
Frame: Frames are often made from galvanized steel, plastic, or aluminum.
Support Grids: Provide structure to prevent the pockets from collapsing.
Pocket filters are installed in HVAC systems to trap contaminants and prevent them from circulating in the indoor environment. As air flows through the pockets, particulates are captured by the filter media, while clean air is pushed out into the space.
Stages of Filtration in HVAC Systems
Primary Filter: A coarse filter captures larger dust particles to protect downstream filters.
Secondary Filter (Pocket Filter): Filters fine dust and other small particulates, such as pollen or mold spores.
HEPA or ULPA Filters (Optional): Used in environments requiring ultra-clean air, like hospitals or cleanrooms.
1. High-Efficiency Filtration
Pocket filters are known for their high efficiency in capturing small particulates. They are available in various grades, including F7, F8, and F9 filter grades, ensuring compliance with both ISO ePM1 / ePM2.5 standards and EN779 classifications.
2. Improved Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
Pocket filters significantly enhance indoor air quality, helping reduce allergens, pollutants, and airborne bacteria, which is essential in hospitals, schools, and office buildings.
3. Energy Savings and Airflow Optimization
With their low resistance to airflow, pocket filters allow HVAC systems to operate efficiently, reducing energy consumption and lowering operational costs.
4. Extended Lifespan and Cost Efficiency
The pleated filter bags in pocket filters can hold more dust compared to flat-panel filters. This minimizes the frequency of filter bag replacements and reduces maintenance costs.
Standard Pocket Filters:
Designed for general HVAC applications.
Available in F7 to F9 grades for different filtration needs.
V-Bank Pocket Filters:
Compact design with a V-shape to fit into tight spaces.
Provides high airflow capacity and energy savings.
Synthetic Media Pocket Filters:
Made from synthetic fibers for enhanced durability.
Ideal for environments with high humidity.
Fiberglass Pocket Filters:
Composed of glass fibers for better fire resistance.
Common in industrial settings.
1. Air Handling Units (AHUs)
Pocket filters are a critical component in AHUs, ensuring that only clean air circulates through HVAC ducts.
2. Cleanrooms and Laboratories
These filters help maintain strict air quality standards required for sensitive manufacturing processes, such as pharmaceuticals or microelectronics.
3. Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities
Pocket filters play a key role in reducing airborne bacteria and ensuring healthy environments for patients and staff.
4. Office Buildings and Schools
With an increasing focus on IAQ, pocket filters help reduce allergens and pollutants, contributing to a healthier workplace and learning environment.
When selecting a pocket filter, it is essential to understand relevant air quality standards.
ISO 16890: This standard classifies filters based on their efficiency in capturing PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 particles.
EN779: The previous standard focused on efficiency classifications such as F7, F8, and F9 grades, which are still relevant in many industries.
Determine Filtration Requirements: Identify the types of particles (e.g., dust, pollen, bacteria) you need to filter out.
Select the Appropriate Filter Grade: Use ISO ePM1 for critical environments and ePM2.5 for general applications.
Consider Energy Efficiency: Choose a low-resistance filter to optimize airflow and reduce energy costs.
Check Compatibility with Standards: Ensure compliance with EN779 or ISO 16890.
When to Replace a Pocket Filter
When airflow resistance increases.
When IAQ sensors detect poor air quality.
As recommended by the manufacturer, typically every 3–6 months.
Tips for Maintaining Pocket Filters
Inspect Filters Regularly: Look for dust buildup or signs of wear.
Monitor Pressure Drops: Use sensors to track airflow changes.
Replace Filter Bags Promptly: Delayed filter bag replacements can strain the HVAC system.
Higher Dust-Holding Capacity: The multi-pocket design allows for greater dust accumulation.
Longer Lifespan: Requires fewer replacements compared to flat-panel filters.
Versatility: Available in various grades and sizes for different applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Pocket filters can contribute to sustainable building operations by improving HVAC efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Additionally, filters with replaceable bags generate less waste, supporting eco-friendly practices.
Pocket filters are essential for maintaining healthy indoor environments and ensuring the efficient operation of HVAC systems. Whether you need clean air for an office, school, or industrial setting, pocket filters offer a versatile solution that combines high-efficiency filtration with energy savings.
By selecting the right filter grade—such as F7, F8, or F9—and ensuring compliance with ISO 16890 standards, you can optimize your HVAC system and improve IAQ. With proper maintenance and timely filter bag replacements, pocket filters provide a long-lasting, cost-effective solution for air filtration.
Invest in pocket filters today to protect your indoor environment and create a sustainable future. Clean air is not just a necessity—it’s a commitment to health, comfort, and energy efficiency.
- How often should pocket filters be replaced?
Typically every 3–6 months, depending on usage and environment.
- What are the benefits of V-bank pocket filters?
They offer high airflow capacity in a compact design, ideal for space-constrained areas.
- Do pocket filters improve energy efficiency?
Yes, their low resistance helps HVAC systems operate more efficiently, reducing energy costs.
- Are pocket filters eco-friendly?
Some models with replaceable filter bags generate less waste, supporting sustainability.